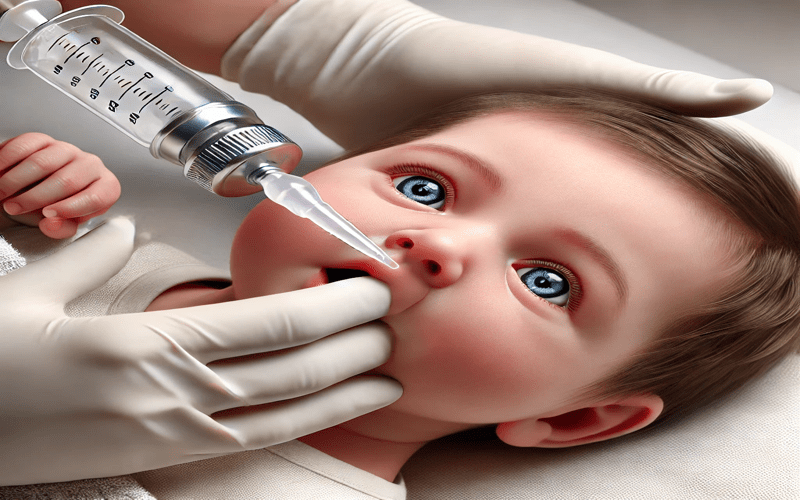
1.Introduction
A newborn’s ability to breathe properly is vital for their health and comfort. Suctioning the mouth before the nose is a simple yet essential step to prevent choking and keep the airways clear. If the nose is suctioned first, mucus can be pushed into the throat, making breathing harder. Using the correct technique ensures your baby breathes easily and stays safe. In this guide, we’ll explore why suction mouth before nose in newborn care is the golden rule and how to do it properly for your little one’s well-being.
2.The Golden Rule: Mouth Before Nose – Why It’s Crucial for Newborns
When a baby is born, their first few breaths are critical. If mucus or amniotic fluid is blocking their airway, they may struggle to breathe properly. That’s why doctors and nurses follow a simple but essential rule:
Always suction the mouth before the nose
But why suction mouth before nose in newborn care? This article explains the medical reason, how newborn anatomy affects breathing, and why this technique is vital for your baby’s safety.
Medical Guideline: Why Doctors and Nurses Always Suction the Mouth First
Doctors and nurses are trained to clear a newborn’s airway in the correct order to prevent complications. According to medical guidelines:
Step 1: Suction the mouth first.
Step 2: Suction the nose afterward.
This sequence is followed because:
Prevents Aspiration (Fluid Entering the Lungs)
If the nose is suctioned first, the baby might take a sudden deep breath. If there’s still mucus in their mouth, they could accidentally inhale it into their lungs, leading to serious breathing problems or even pneumonia. This is why suction mouth before nose in newborn care is the golden rule. By clearing the mouth first, we ensure that the baby doesn’t inhale mucus when they take their first breaths.
Avoids Choking and Gagging
Newborns have a strong gag reflex. If mucus is left in the mouth, it can cause choking. By suctioning the mouth before the nose, we reduce the risk of gagging, making breathing easier for the baby.
Ensures a Clear Airway for Proper Breathing
Newborns naturally breathe through their noses, but if their mouth is full of mucus, it can still block airflow. Clearing the mouth first ensures that air can flow freely through both the mouth and nose.
How a Newborn’s Anatomy Affects Breathing and Suctioning
A newborn’s airway is very small and can easily become blocked. This is why suctioning must be done correctly.
Babies Are Obligate Nose Breathers
Newborns primarily breathe through their noses. However, if mucus is present in the mouth, they might try to breathe through it, which can lead to mucus being inhaled into the lungs. By clearing the mouth first, we ensure that the baby can breathe safely and naturally.
Small Airways Get Blocked Quickly
Newborns have tiny airways that can easily be blocked by mucus. Why suction mouth before nose in newborn care? Suctioning the mouth first prevents mucus from being pulled into the airway, ensuring smooth breathing. Following this order helps keep your baby safe.
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Properly Suction a Newborn
If you need to suction your newborn at home due to excess mucus, follow these steps:
Step 1: Get a Bulb Syringe or Suction Device
- Use a clean bulb syringe or a medical-grade suction device.
Step 2: Squeeze the Bulb Before Inserting
- This creates suction when you release it.
Step 3: Insert the Tip into the Baby’s Mouth First
- Place it inside the cheek, not directly in the throat.
Step 4: Release the Bulb to Remove Mucus
- Gently pull out the mucus without causing discomfort.
Step 5: Repeat for the Nose (One Nostril at a Time)
- Once the mouth is clear, suction each nostril gently to remove mucus.
Step 6: Clean the Bulb Syringe After Use
- Wash and sterilize the suction device to keep it hygienic.
3.Why Suctioning the Mouth First is Crucial for Newborns
A newborn’s first few breaths are critical. If their airway is blocked by mucus or amniotic fluid, they may struggle to breathe properly. That’s why doctors and nurses always suction the mouth before the nose. But why suction mouth before nose in newborn care?. This article explains the importance of suctioning order, how it helps prevent aspiration and choking, and why keeping a newborn’s airway clear is essential for breathing and feeding.
If your baby keeps rolling over in sleep and waking up, it can disrupt their rest and cause frustration. Learn why this happens, how to keep them safe, and tips to improve sleep.
Preventing Aspiration and Choking Risks
One of the biggest dangers for newborns during delivery is aspiration—when fluid or mucus enters the lungs, causing serious breathing issues or even pneumonia. This is why suction mouth before nose in newborn care is essential. Clearing the mouth first prevents mucus from being inhaled, ensuring safe and smooth breathing.
Why does suctioning the mouth first help?
If the nose is suctioned first, the baby might take a sudden breath.
This can cause any remaining mucus in the mouth to be inhaled into the lungs.
By clearing the mouth first, we prevent the risk of the baby accidentally pulling fluid into their airway.
Choking Hazard
Newborns have a strong gag reflex. If there is mucus in their mouth, they can start choking. By suctioning the mouth first, we reduce this risk and help the baby breathe more easily.
Ensuring the Airway Remains Clear for Effective Breathing
A newborn’s breathing pattern is different from adults. Babies are obligate nose breathers, meaning they naturally breathe through their nose most of the time. However, this doesn’t mean the mouth isn’t important for breathing. If the mouth is full of mucus, it can still block airflow, making it harder for the baby to breathe.
Why Mouth First?
Clearing the mouth ensures there are no obstructions before the baby starts taking deep breaths.
Newborns have small airways, so even a little mucus can block them.
Proper suctioning helps oxygen flow smoothly, preventing breathing difficulties.
If the order is reversed (nose first, mouth second), the baby might try to inhale through the mouth, pulling mucus deeper into their throat or lungs.
How Mucus Buildup Can Impact Feeding and Breathing
Newborns rely on a clear airway not just for breathing but also for feeding. If there is mucus buildup in the mouth, it can make it harder for them to latch onto the breast or bottle properly.
Problems Caused by Mucus in the Mouth:
Difficulty sucking and swallowing milk
Increased risk of spitting up or choking
Discomfort while feeding, leading to fussiness
Interrupted breathing patterns
By suctioning the mouth first, we help the baby:
Breathe better during feeding
Swallow milk properly without choking
Stay comfortable and feed efficiently
Step-by-Step Guide: How to Properly Suction a Newborn
If you need to suction your newborn at home, follow these simple steps:
Step 1: Use a Bulb Syringe or Suction Device
- Choose a soft bulb syringe or a medical suction device for safety.
Step 2: Squeeze the Bulb Before Inserting
- This creates the suction effect needed to remove mucus.
Step 3: Gently Insert the Tip into the Baby’s Mouth First
- Aim for the side of the cheek, not the throat, to remove mucus safely.
Step 4: Release the Bulb to Pull Out Mucus
- Slowly remove mucus without causing discomfort.
Step 5: Suction the Nose After the Mouth is Clear
- Once the mouth is cleared, repeat the process for each nostril one at a time.
Step 6: Clean the Syringe After Each Use
- Wash and sterilize the suction device to keep it hygienic.
4.Step-by-Step Guide to Proper Suctioning for Newborns
Newborns often have mucus buildup in their airways, which can make breathing or feeding difficult. Proper suctioning helps clear their mouth and nose, ensuring safe and comfortable breathing. However, it’s important to follow the correct technique to avoid harming their delicate tissues.
One key rule in newborn suctioning is to always clear the mouth before the nose. But why suction mouth before nose in newborn care? Suctioning the nose first can make a baby gasp, potentially inhaling mucus deeper into the lungs. That’s why doctors and nurses always follow the Mouth Before Nose Rule for safe and effective suctioning.
This guide will show you:
How to use a bulb syringe or suction catheter correctly
How to avoid hurting delicate newborn tissues
Signs that indicate your baby needs suctioning
5.Safe and Correct Use of a Bulb Syringe or Suction Catheter
Choosing the Right Suctioning Tool
There are two main tools used for newborn suctioning:
Bulb Syringe – A soft, rubber bulb that creates gentle suction. This is commonly used at home and in hospitals.
Suction Catheter – A medical tube used for deeper suctioning, typically in hospitals under professional supervision.
For parents, a bulb syringe is the safest and easiest option for home use.
Step-by-Step Guide to Proper Suctioning
Step 1: Wash Your Hands & Prepare the Bulb Syringe
- Hygiene is important! Wash your hands thoroughly with soap.
- Squeeze the bulb before inserting it to create suction.
Step 2: Suction the Mouth First (Golden Rule: Mouth Before Nose!)
- Gently place the tip inside the baby’s cheek, not the throat.
- Slowly release the bulb to remove mucus.
- Why suction mouth before nose in newborn care? If the nose is suctioned first, the baby might inhale mucus deeper into their lungs.
Step 3: Suction the Nose Second
- After clearing the mouth, squeeze the bulb again to remove trapped air.
- Insert the tip just inside the nostril (not too deep).
- Gently release the bulb to remove mucus.
Step 4: Clean the Bulb Syringe After Each Use
- Wash it with warm, soapy water.
- Allow it to dry completely in the open air before using it again.
How to Avoid Harming Delicate Newborn Tissues
Newborns have very sensitive airways, so suctioning must be gentle and precise. Here’s how to protect your baby:
Don’t suction too frequently. Over-suctioning can cause swelling and irritation inside the nose.
Never insert the bulb syringe too deep. Always place it just at the entrance of the mouth or nostrils.
Use gentle suction pressure. Too much force can make the baby uncomfortable.
Use saline drops if needed. If the mucus is thick, saline drops can help loosen it before suctioning.
Using the right technique ensures that suctioning is safe, effective, and comfortable for your newborn.
Signs That Indicate Your Baby Needs Suctioning
Babies cannot clear their throats or blow their noses like adults. Here are signs that your newborn may need suctioning:
Noisy breathing – Whistling, snorting, or gurgling sounds when breathing.
Difficulty feeding – Baby struggles to suck or keeps pulling away from the breast/bottle.
Frequent coughing or gagging – Excess mucus can make a newborn gag or choke.
Flaring nostrils or chest retractions – Signs of labored breathing.
Trouble breathing – If your baby looks uncomfortable or is gasping for air.
Seek medical help immediately if your baby’s breathing problems persist! If your newborn turns blue, stops breathing momentarily, or struggles even after suctioning, go to the nearest hospital.
6.When to Seek Medical Help for Newborn Breathing Issues
Newborns rely on clear airways for smooth breathing and feeding. While suctioning can help remove excess mucus, some situations require immediate medical attention. It’s essential for parents to recognize when a baby’s breathing problems are serious and need professional care.
One important factor in newborn suctioning is understanding why suction mouth before nose in newborn care is critical. If the nose is suctioned first, the baby may gasp for air, pulling mucus deeper into the lungs and making breathing even more difficult.
This section will cover:
Warning signs of respiratory distress
How excessive mucus could indicate an underlying condition
When to seek professional medical help
Warning Signs of Respiratory Distress
Breathing problems in newborns can escalate quickly. If you observe any of these signs, reach out to your pediatrician without delay.
Fast breathing (over 60 breaths per minute)
Flaring nostrils (a sign of struggling for air)
Chest retractions (skin pulling between ribs with each breath)
Blue lips or pale skin (oxygen deprivation warning)
Long pauses in breathing (apnea episodes)
If any of these signs appear, do not wait—seek medical attention immediately.
How Excessive Mucus Could Indicate an Underlying Condition
While normal mucus buildup can be managed with suctioning, excessive mucus could be a symptom of a larger issue:
Respiratory Infections – Colds, flu, or RSV can cause congestion and breathing difficulties.
Reflux (GERD) – Some newborns develop congestion due to stomach acid affecting the airways.
Allergies or Irritants – Exposure to dust, smoke, or strong smells can lead to mucus overproduction.
Premature Lung Development – Preterm babies may have weaker lungs, making mucus clearance harder.
If you’re frequently needing to suction your baby’s airways and mucus is thick, yellow, or green, consult a doctor as it may indicate an infection.
When to Seek Professional Medical Intervention
Some breathing difficulties cannot be managed at home and require urgent care. Go to the hospital immediately if:
Your baby struggles to breathe even after suctioning.
Feeding becomes difficult due to excessive mucus.
There is blood in the mucus after suctioning.
Your baby turns blue or pale.
Understanding why suction mouth before nose in newborn care is crucial in preventing serious complications. If suctioning does not improve your baby’s breathing, seek medical help immediately.
Alternative Methods for Clearing Mucus in Newborns
Newborns often struggle with mucus buildup, which can make breathing and feeding difficult. While suctioning is a common method, there are natural ways to help clear a baby’s airways without using a bulb syringe or suction device.
Key natural methods include:
Humidifiers to loosen mucus
Proper positioning to help drainage
Breastfeeding for natural mucus clearance
Understanding why suction mouth before nose in newborn care is important, but these alternative methods can also provide relief and improve your baby’s comfort.
Using Humidifiers to Loosen Mucus
Dry air can thicken mucus, making it harder for a baby to breathe. A humidifier increases air moisture, which helps to:
Thin out mucus, making it easier to drain
Prevent congestion from getting worse
Soothe irritated nasal passages
For best results:
Use a cool-mist humidifier (warm mist can be unsafe for babies).
Place it near the baby’s crib, but not too close.
Clean the humidifier every day to avoid the growth of mold and bacteria.
Using a humidifier along with proper suctioning techniques ensures that mucus doesn’t block the baby’s airways. That’s why medical experts emphasize why suction mouth before nose in newborn care—it prevents mucus from moving deeper into the lungs.
Proper Positioning for Better Drainage
The way you position your baby can help mucus drain naturally and reduce congestion.
Elevate the Head Slightly – Keeping your baby’s head slightly raised (e.g., by holding them upright or placing a small towel under the crib mattress) helps mucus drain instead of pooling in the throat.
Tummy Time – Giving your baby some tummy time while they’re awake can:
Help loosen mucus naturally
Encourage them to cough up excess mucus
Strengthen neck and chest muscles for better breathing
Positioning plays a major role in mucus clearance, but if your baby is still struggling, remember why suction mouth before nose in newborn care—suctioning the mouth first prevents mucus from being inhaled deeper into the lungs.
The Role of Breastfeeding in Clearing Congestion
Breastfeeding is not just for nutrition—it also helps with mucus clearance. Breast milk contains antibodies that fight infections and can:
Thin out mucus, making it easier for your baby to swallow and breathe comfortably.
Provide hydration, which keeps airways moist and prevents mucus from thickening
Strengthen the immune system, reducing the chances of infections that cause congestion
If your baby is congested, try nursing more frequently. The sucking motion also helps clear nasal passages by naturally promoting mucus drainage.
7.Common Mistakes to Avoid When Suctioning a Newborn
Clearing mucus from a newborn’s airways is essential for smooth breathing and feeding, but many parents unknowingly make mistakes while using a suction bulb or catheter. If done incorrectly, suctioning can cause discomfort, irritation, and even breathing issues for your baby.
In this section, we’ll discuss:
The risks of over-suctioning
Why using the right tools matters
Misconceptions about newborn congestion
Understanding why suction mouth before nose in newborn care is critical to avoiding these mistakes and ensuring your baby’s safety.
Over-Suctioning and Its Risks
Many parents believe that frequent suctioning keeps their baby’s airways clear at all times. However, too much suctioning can:
Irritate delicate nasal and throat tissues
Cause swelling, making breathing even harder
Increase mucus production as the body tries to compensate
How often should you suction?
Only when your baby is struggling to breathe due to mucus buildup.
Typically before feeding and sleep to help with comfort.
No more than 2-3 times per day, unless advised by a doctor.
Overdoing it can make congestion worse, so always remember why suction mouth before nose in newborn care—it’s a gentle process meant to help breathing, not harm delicate tissues.
Using Inappropriate Tools for Suctioning
Not all suctioning tools are safe or effective for newborns. Some parents use:
Adult nasal aspirators, which are too powerful for delicate newborn airways.
Cotton swabs or tissues, which can push mucus deeper instead of removing it.
Homemade suction devices, which may be unsanitary or too harsh.
Best suctioning tools for newborns:
Bulb syringe – Simple, gentle, and easy to use.
Nasal aspirators (like NoseFrida) – Controlled suction that’s safe for newborns.
Saline drops – Helps loosen mucus naturally before suctioning.
Using the right tools ensures safe and effective mucus removal. Again, always follow the golden rule: why suction mouth before nose in newborn care to prevent mucus from being inhaled deeper into the lungs.
Misconceptions About Newborn Congestion
Many parents panic when they hear their newborn making snorting or grunting noises, assuming they are congested. But not all newborn noises mean there’s a problem!
Common misconceptions:
If my baby sounds congested, I must suction right away.
Newborns naturally have small nasal passages, so mild congestion is normal. Only suction if mucus is visibly blocking the nose or causing breathing issues.
Suctioning will stop my baby’s congestion permanently.
Suctioning only removes existing mucus. It does not prevent future congestion, which can happen due to colds, dry air, or natural mucus production.
Suctioning is always safe, no matter how often I do it.
Overuse can irritate airways and make congestion worse. Stick to gentle and occasional suctioning as needed.
By understanding why suction mouth before nose in newborn care, parents can avoid unnecessary suctioning and use safer, alternative methods like humidifiers or saline drops when needed.
Conclusion
Suctioning the mouth before the nose in newborn care is essential to prevent choking, clear airways, and ensure smooth breathing. If the nose is suctioned first, mucus can be pushed into the throat, increasing the risk of aspiration. Using a bulb syringe or nasal aspirator gently, limiting suctioning to avoid irritation, and using saline drops to loosen mucus can help keep your baby comfortable. If your newborn struggles to breathe, seek medical advice. Knowing why suction mouth before nose in newborn care helps parents protect their baby’s health and safety.
FAQS
1. Do you suction a baby’s mouth or nose first?
Always suction the mouth first, then the nose. This prevents the baby from inhaling mucus into the lungs, reducing the risk of breathing issues.
2. Why would a nurse perform nasal and oral suctioning on a newborn?
A nurse suctions a newborn to clear mucus, help with breathing, and prevent aspiration, especially after birth.
3. What is the purpose of oral and nasal suctioning?
Suctioning removes excess mucus and fluids, ensuring clear airways for smooth breathing.
4. What is the correct technique for suctioning a newborn?
Use a bulb syringe or suction catheter, gently suction the mouth first, then the nose, and avoid over-suctioning to prevent irritation.
